Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a form of psychological treatment that has been shown to be effective for a range of problems including depression, anxiety disorders, relational struggles, and so on. Numerous research studies suggest that CBT can lead to significant improvement in functioning and quality of life.
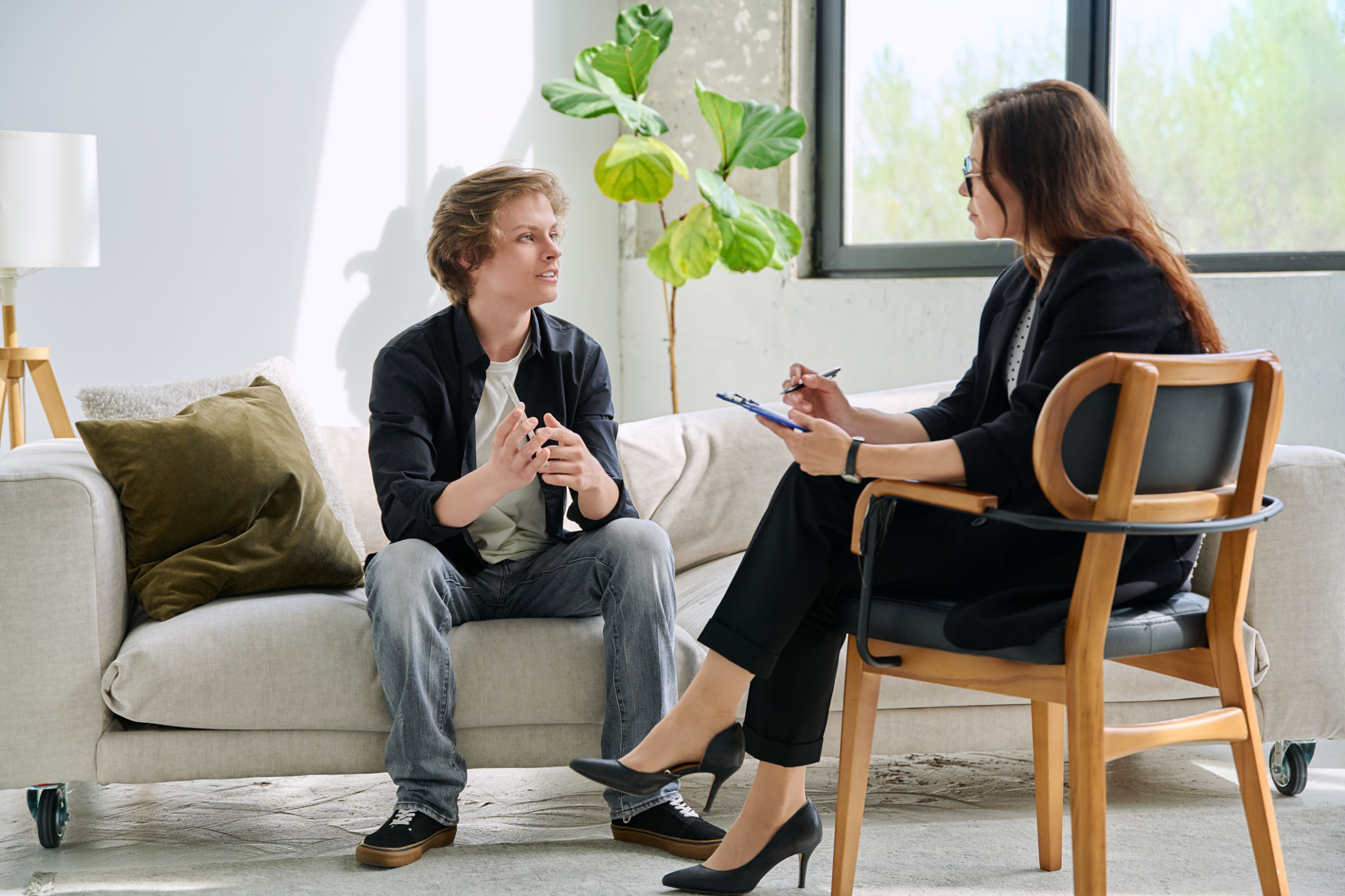

CBT focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to an individual's difficulties. It is a structured, goal-oriented therapy that requires active participation from the client and typically works for individuals seeking a more solution focused approach in therapy. This approach is distinct from other forms of therapy as it often involves homework assignments outside of sessions to reinforce what is learned during therapy.
The Core Principles of CBT
Cognitive Restructuring
One of the main principles of CBT is the concept of cognitive restructuring. This involves identifying and challenging distorted or unhelpful thinking patterns. The goal is to gently engage our capacity for nuance to potentially replace difficult thoughts with more balanced and realistic ones. By doing this, individuals can impact their emotional responses and behaviors.
Behavioral Activation
Behavioral activation is another key component of CBT. It involves helping individuals engage in activities that are likely to improve their mood and overall well-being. Often, when people feel depressed or anxious, they may withdraw from activities they once enjoyed. Behavioral activation encourages them to re-engage with these activities in whatever capacity they realistically can.

The Process of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Initial Assessment
During the initial assessment, the therapist and client work together to identify specific problems and goals for therapy. This stage is crucial as it sets the direction for treatment and determines the areas that need focus.
Goal Setting
Once the issues are identified, setting achievable goals becomes the next step. These goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). By having clear goals, both the therapist and client can track progress throughout the therapy process.
Benefits of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
CBT has been found to be effective in treating a variety of conditions. Some benefits include:
- Improved communication and problem-solving skills
- Better understanding and management of emotions
- Reduction in symptoms of mental health disorders
Moreover, CBT equips individuals with self-help tools that can be used long after therapy has ended. This empowers clients to maintain improvements and manage potential future challenges independently.
Conclusion
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is a powerful tool that provides individuals with the skills needed to overcome mental health difficulties. By focusing on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors, CBT helps clients achieve a nuanced, more balanced state of mind. If you're considering therapy, CBT might be an effective option for achieving your mental health goals.
